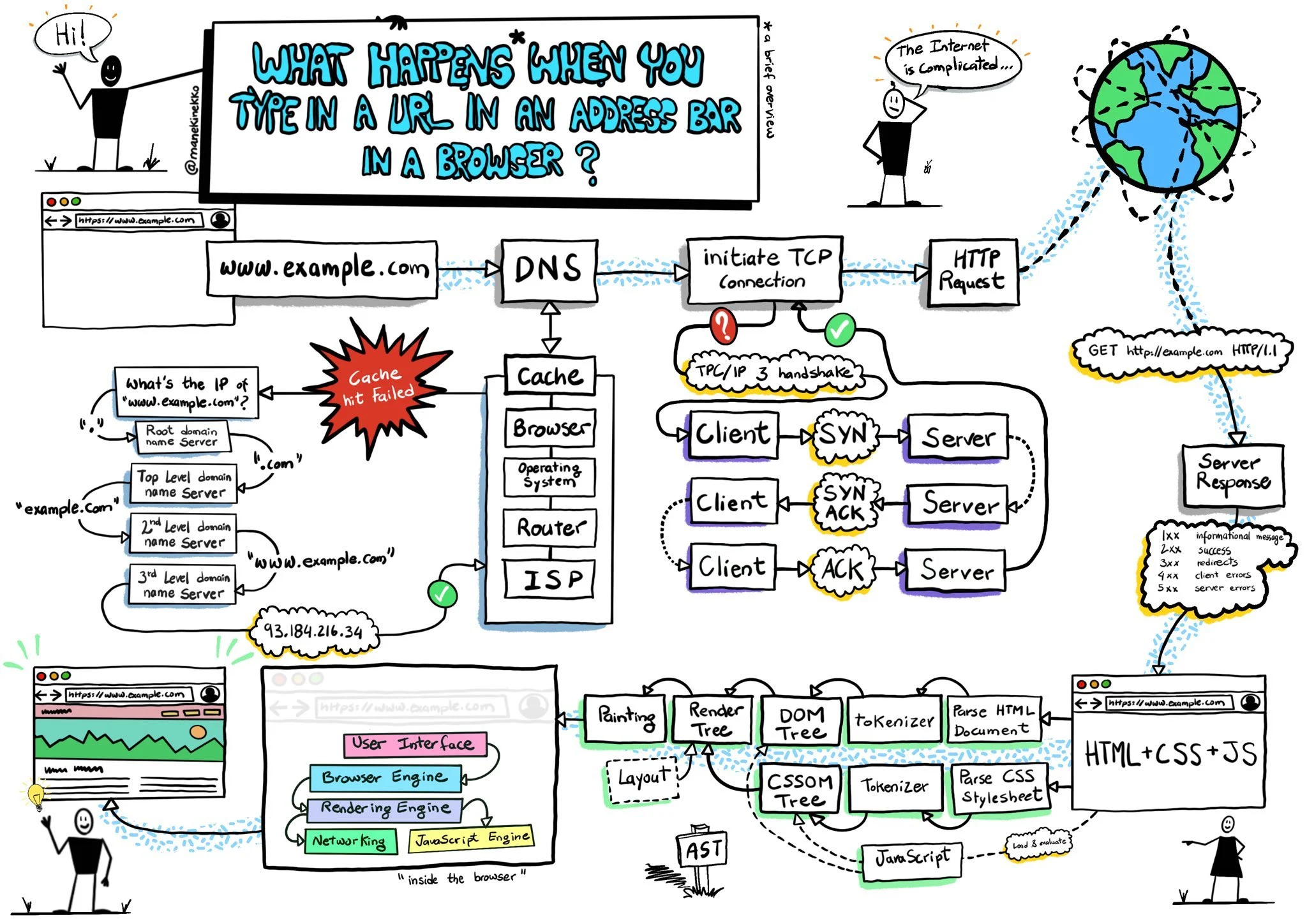
Very instructive don’t you think? Kudos for Kamran Ahmed @kamranahmedse
Here are the technical terms defined as simple as possible:
DNS – Domain Name System: In very simple terms, it translates domain names like www.example.com to a number like 93.184.216.34 that corresponds with a computer on the internet somewhere.
CACHE – a holding area in computer memory where often- or most-recently used things are quickly available .
ROUTER – A router is hardware used to connect two or more computers to each other, and usually to the Internet, by wire or sometimes radio signals (like Wi-Fi).
TCP – Transmission Control Protocol. This is the protocol that the Internet uses to transport data packets from one computer to another.
HTTP – Hypertext Transfer Protocol is the way data gets sent and received in the World Wide Web, where hypertext documents include links to other resources that you can easily access with a click.
SYN/ACK – How two computers on the internet start talking to each other using TCP.
HTML – Hyper Text Markup Language, how webpages are being painted on the screen of your browser.
CSS – Cascading Style Sheets describe how the webpage you just pulled up should look like.
JS – JavaScript, a programming language that helps build the webpage on your browser screen.
Tokenizer – a tokenizer helps building your webpage by recognizing incoming data by looking for whitespace like tabs, spaces, and new lines.
DOM TREE and CSSOM Tree – You may know that HTML is actually a bunch of text tags like <head> or <body>. To paint a webpage, these tags are organized in trees so that they can easily be painted on the screen, which is called rendering. Here is an example of one of those trees. And that his is all you need to know for the moment! WHEW.
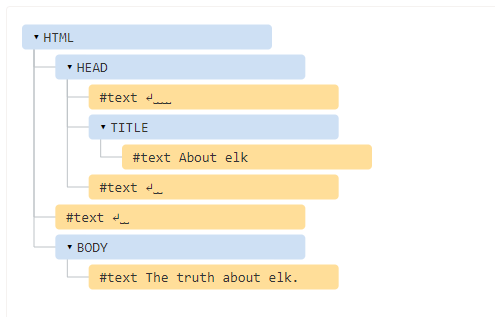
As you can see, pretty complicated stuff that goes on under the hood. Lots of stuff can fall over. Turning the system off and back on often solves a lot of issues. 😀